Interesting scientific latest research. Scientific news
In order to successfully create new inventions, or at least have time to follow them, you simply need to know what our modernity stands on, that is, science, technology and infrastructure. These are the most important inventions and discoveries, the significance of which cannot be overestimated.
Fire
It is not known exactly when people began to use fire, when they learned to store or produce it, but scientists suggest that all this happened from 600 to 200 thousand years ago.
Language

The first oral speech with semantic and phonetic structures appeared about ten thousand years ago.
Trade (barter)

The first case of barter exchange was traced in the Papua New Guinea region about 19 thousand years ago. By the third millennium BC. e. Trade routes appeared in Asia and the Middle East.
Agriculture and farming

About 17 thousand years ago, people first began to domesticate animals, and in the tenth millennium BC. e. began to grow plants, which led to the formation of permanent settlements and the end of the nomadic lifestyle.
Ship

Around the fourth millennium BC. e. in ancient Egypt they began to use wooden rafts and boats, and in the 12th century BC. e. The Phoenicians and Greeks began to build ships, which allowed not only to expand the world of that time, but also to develop trade, science, geography and cartography.
Wheel

The wheel became one of the simplest and most important inventions in human history. They started using it about five thousand years ago.
Money

A new step in the development of trade was the use of money. They were first used by the Sumerians in the third millennium BC. e.
Iron

Metallurgy began its development with the use of copper, silver and tin. Bronze followed. In the third millennium BC. e. people began to use stronger iron.
Written speech

Although spoken language has existed for thousands of years, writing first appeared among the Sumerians only five thousand years ago.
Legislation

In the 18th century BC. e. Hammurabi, the sixth Babylonian king, wrote his famous code, or collection of laws by which society was supposed to live. Other examples of ancient legal texts are the Book of the Dead, the Ten Commandments, and the Book of Leviticus.
Alphabet
The first alphabet containing both vowels and consonants appeared among the Phoenicians in 1050 BC. e.
Steel
Steel alloys are rightfully considered the strongest. Steel was first used in Asia about four thousand years ago. The Greeks began using these alloys in the 7th century BC. e., 250 years before China and Rome.
Hydropower

The energy of flowing or falling water began to be used in the Mesopotamia region in the 2nd century BC. e.
Paper

The Chinese first began using paper around 105 AD. e., it was fabric. Paper made from wood appeared only in the 16th century.
Manual typing using movable characters
![]()
Although the invention of the printing press is credited to Gutenberg (1436), the technology on which it is based originates from China. Movable type was invented by Bi Shen in 1040.
Microscope
In 1592, optical masters from Holland Zacharias and Hans first saw that objects could be seen much closer through certain lenses. It was these special lenses that made it into the first microscope.
Electricity

In 1600, Englishman William Gilbert first used the term "electricity". In 1752, Benjamin Franklin proved that lightning is electricity.
Telescope
In 1608, Hans Lippershey created a converging lens, which he inserted into a spyglass. This became the prototype for the telescope, which Galileo improved a year later.
Engine

The invention of the steam engine by Thomas Newcomen in 1712 was the next giant step in technological development. The internal combustion engine was invented by Etienne Lenoir in 1858.
Incandescent lamp

The incandescent lamp, which was invented in 1800 by Humphrey Davy and later improved by Thomas Edison, helped turn night into day.
Telegraph
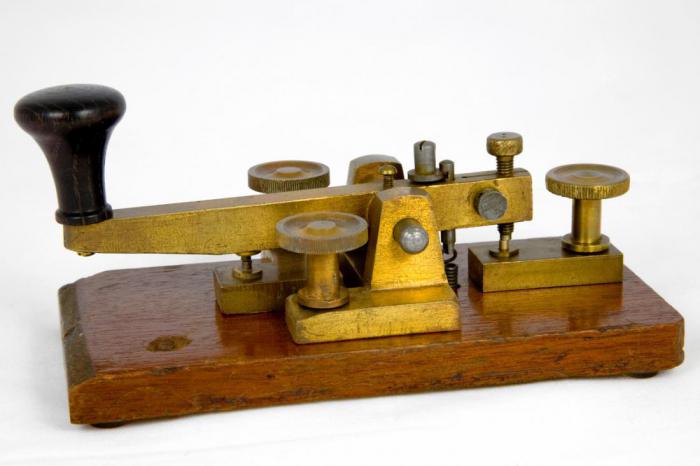

The first simple telegraph was invented by the Bavarian Samuel Semmering in 1809. However, the author of the first commercially successful version of the telegraph is considered to be Samuel Morse, the creator of Morse code.
Electromagnet

William Sturgeon invented the first electromagnet in 1825. His invention consisted of an ordinary iron horseshoe, around which a copper wire was wound.
Oil and gas

This natural fuel was first discovered in 1859. The first gas well was discovered in Ohio, and the first oil well was discovered in Pennsylvania.
Telephone

The first device capable of transmitting distinct sounds was invented in 1860 by the German Philipp Reise. 16 years later, Alexander Bell patented and demonstrated to the public an improved model.
Electric lamp

This vacuum electronic device is based on the fact that the flow of electricity does not need a wire and can pass through both air and vacuum. The first such device was created by Lee de Forest in 1893.
Semiconductors
The first semiconductors were discovered in 1896. Today, the main semiconductor is silicon. It was first used for commercial purposes by Jagadish Chandra Bose.
Penicillin
Everyone has heard about the accidental discovery of the antibiotic penicillin in 1928. However, long before Fleming, these properties were noticed by the French medical student Ernest Duchesne in 1896, but his research went unnoticed.
Radio

Among the inventors of radio are such names as Heinrich Hertz (1888), Thomas Edison (1885) and even Nikola Tesla, who patented his invention in 1897.
Electron
This negatively charged elementary particle was discovered by Joseph Thomson in 1897. The electron is the main carrier of electric charge.
The quantum physics
The real beginning quantum physics It is generally accepted that the year 1900 and Planck's hypothesis. On its basis, Einstein built his theory about particles of light, which were later called photons.
Airplane

The Wright brothers' famous invention dates back to 1903. The first successful manned flight took place on December 17.
A television

Television is based on a number of inventions and discoveries, but the first full-fledged television was created in 1926 by John Logie Baird.
Transistor
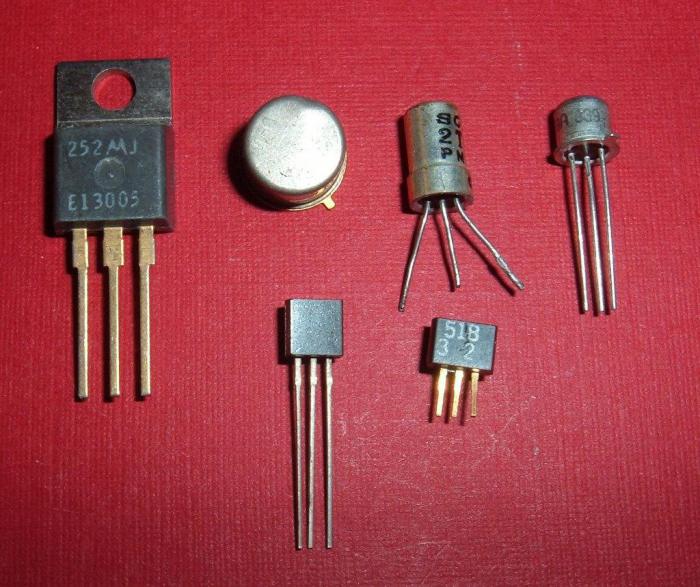

Switching and amplification of an electronic signal is carried out using a transistor - an invention created by Bill Shankly in 1947 and which made it possible to first think about the possibility of creating Global network telecommunications.
DNA

The main secret of life on earth was discovered by a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge in 1953. Watson and Crick received the Nobel Prize for this discovery.
Integrated circuit
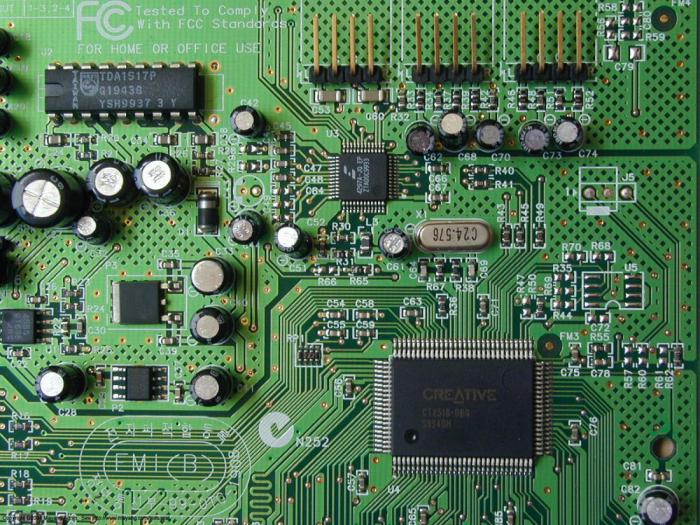

In 1959, through the efforts of several developers, inventors and corporations, the first integrated circuit was created - an arbitrary set of electronic components combined into a single chip or on a single circuit. It was this invention that made it possible to create microchips and microprocessors.
Internet

The progenitor of the Internet was ARPANET, or the DARPA project, developed in 1969. However, modern data transfer protocols and the Internet itself were created in 1991 by the British Tim Berners-Lee.
Microprocessor
In 1971, an Intel developer created an innovative integrated circuit, the size of which was tens of times smaller. It was she who became the first microprocessor.
Mobile phone
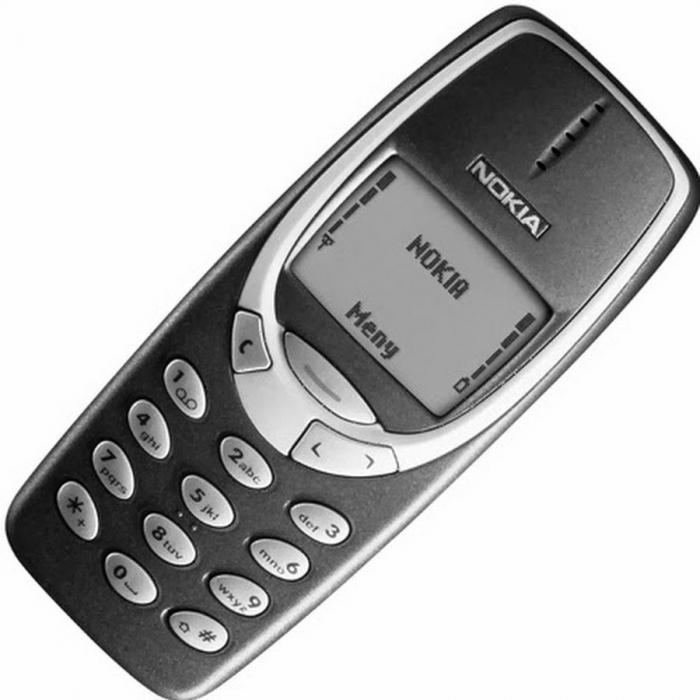

In 1973, Motorola launched the first portable telephone weighing just over a kilogram. Its battery took more than ten hours to charge, and its talk time did not exceed 30 minutes.
Smartphone

In January 2007, Apple released for the first time a phone capable of recognizing multiple touch points. The multi-touch system paved the way for smartphones, tablets and hybrid computers.
Quantum computer

In 2011, D-wave introduced a radically new invention - a quantum computer - computer, based on the phenomena of superposition and entanglement, which makes it thousands of times faster than conventional mechanical computers.
Over the past 10 years, many amazing discoveries and achievements have occurred in the world of science. Surely many of you who read our site have heard about most of the items presented on today’s list. However, their importance is so high that once again it would be a crime not to at least briefly recall them. They need to be remembered at least for the next decade, until new, even more amazing scientific achievements are made on the basis of these discoveries.

Stem cell reprogramming

Stem cells are amazing. They perform the same cellular functions as the rest of the cells in your body, but, unlike the latter, they have one amazing property - if necessary, they are able to change and acquire the function of absolutely any cells. This means that stem cells can be turned into, for example, erythrocytes (red blood cells) if your body lacks them. Or into white blood cells (leukocytes). Or muscle cells. Or neurocytes. Or... in general, you get the idea - in almost all types of cells.
Despite the fact that the general public has known about stem cells since 1981 (although they were discovered much earlier, at the beginning of the 20th century), until 2006 science had no idea that any cells of a living organism can be reprogrammed and transformed into stem cells. Moreover, the method of such transformation turned out to be relatively simple. The first person to figure out this possibility was Japanese scientist Shinya Yamanaka, who turned skin cells into stem cells by adding four specific genes to them. Within two to three weeks from the moment the skin cells turned into stem cells, they could be further transformed into any other type of cell in our body. For regenerative medicine, as you understand, this discovery is one of the most important in modern history, since this area now has a virtually limitless source of cells needed to heal the damage your body has sustained.
Largest black hole ever discovered

The “blob” in the center is our solar system
In 2009, a group of astronomers decided to find out the mass of the black hole S5 0014+81, which at that time had just been discovered. Imagine their surprise when scientists learned that its mass is 10,000 times greater than the mass of the supermassive black hole located at the center of our Milky Way, which actually made it the largest known on earth. this moment black hole in the known universe.
This ultramassive black hole has the mass of 40 billion suns (that is, if you take the mass of the Sun and multiply it by 40 billion, you get the mass of the black hole). No less interesting is the fact that this black hole, according to scientists, was formed during the earliest period of the history of the Universe - just 1.6 billion years after the Big Bang. The discovery of this black hole contributed to the understanding that holes of this size and mass are capable of increasing these figures incredibly quickly.
Memory manipulation

It already sounds like a seed for some Nolan’s “Inception,” but in 2014, scientists Steve Ramirez and Xu Liu manipulated the memory of a laboratory mouse, replacing negative memories with positive ones and vice versa. The researchers implanted special light-sensitive proteins into the mouse's brain and, as you might have guessed, simply shined a light into its eyes.
As a result of the experiment, positive memories were completely replaced by negative ones, which were firmly entrenched in her brain. This discovery opens the door to new treatments for those who suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder or are unable to cope with the emotions of losing loved ones. This discovery promises to lead to even more surprising results in the near future.
Computer chip that imitates the functioning of the human brain

This was considered something fantastic just a few years ago, but in 2014, IBM introduced the world to a computer chip that works on the principle human brain. With 5.4 billion transistors and requiring 10,000 times less power to operate than conventional computer chips, the SyNAPSE chip is capable of simulating the functioning of your brain's synapses. 256 synapses, to be exact. They can be programmed to perform any computing task, which can make them extremely useful for use in supercomputers and various types distributed sensors.
Thanks to its unique architecture, the effectiveness of the SyNAPSE chip is not limited to the performance that we are used to evaluating in regular computers. It comes into operation only when necessary, which allows you to significantly save on energy and maintain operating temperatures. This revolutionary technology could truly change the entire computer industry over time.
One step closer to robot dominance

Also in 2014, 1,024 tiny robots called “kilobots” were tasked with combining into the shape of a star. Without any additional instructions, the robots independently and jointly began to complete the task. Slowly, hesitantly, colliding with each other several times, but they still completed the task assigned to them. If one of the robots got stuck or “lost”, not knowing where to go, neighboring robots came to the rescue and helped the “lost” ones find their way.
What is the achievement? Everything is very simple. Now imagine that the same robots, only thousands of times smaller in size, are introduced into your circulatory system and, united, are sent to fight some serious disease that has settled in your body. Larger robots, also teaming up, are sent on some kind of search and rescue operation, and even larger ones are used for the fantastically fast construction of new buildings. Here, of course, one can recall some script for a summer blockbuster, but why escalate it?
Confirmation of dark matter

According to scientists, this mysterious matter may contain answers that explain many as yet unexplained astronomical phenomena. Here is one of them as an example: let’s say, in front of us is a galaxy with the mass of thousands of planets. If we compare the actual mass of these planets and the mass of the entire galaxy, the numbers do not add up. Why? Because the answer goes much deeper than simply calculating the mass of matter that we can see. There is also matter that we are not able to see. This is precisely what is called “dark matter”.
In 2009, several American laboratories announced the discovery of dark matter using sensors immersed in an iron mine to a depth of about 1 kilometer. Scientists were able to determine the presence of two particles whose characteristics correspond to the previously proposed description of dark matter. There's a lot of double-checking to be done next, but everything points to these particles actually being dark matter particles. This may be one of the most amazing and significant discoveries in physics over the last century.
Is there life on Mars?

Maybe. In 2015, NASA published photographs of Martian mountains with dark stripes at their base (photo above). They appear and disappear depending on the season. The fact is that these stripes are irrefutable evidence of the presence of liquid water on Mars. Scientists cannot say with absolute certainty whether the planet had such features in the past, but the presence of water on the planet now opens up many prospects.
For example, the presence of water on the planet can be of great help when humanity finally assembles a manned mission to Mars (sometime after 2024, according to the most optimistic forecasts). In this case, astronauts will have to carry much fewer resources with them, since everything they need is already available on the Martian surface.
Reusable rockets

The private aerospace company SpaceX, owned by billionaire Elon Musk, was able, after several attempts, to soft-land a spent rocket onto a remotely controlled floating barge in the ocean.
Everything went so smoothly that the landing of spent rockets for SpaceX is now being considered routine task. It also allows the company to save billions of dollars in rocket production costs, since they can now be simply rebuilt, re-fueled, and reused (more than once, in theory), instead of just being sunk somewhere in the Pacific Ocean. Thanks to these rockets, humanity has immediately become several steps closer to manned flights to Mars.
Gravitational waves

Gravitational waves are ripples in space and time that travel at the speed of light. They were predicted by Albert Einstein in his general theory of relativity, according to which mass can bend space and time. Gravitational waves can be created by black holes, and they were detected in 2016 using the high-tech equipment of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, or simply LIGO, thereby confirming Einstein's century-old theory.
It's really very important discovery for astronomy, since it proves much of Einstein's general theory of relativity and allows, with the help of instruments such as LIGO, the prospect of detecting and monitoring events of enormous cosmic proportions.
TRAPPIST system

TRAPPIST-1 is star system, located approximately 39 light years from our solar system. What makes her special? Not much, unless you consider its star, which has 12 times less mass than our Sun, and at least 7 planets orbiting it and located in the so-called Goldilocks zone, where life could potentially exist.
As expected, there is now heated debate around this discovery. It even goes so far as to claim that the system may not be at all suitable for life and its planets look more like unsightly, worn-out cosmic boulders than our future interplanetary resorts. Nevertheless, the system deserves absolutely all the attention that is now focused on it. Firstly, it is not so far from us - only some 39 light years from the Solar System. On a cosmic scale - around the corner. Secondly, it has three Earth-like planets located in the habitable zone and are perhaps the best targets today for the search for extraterrestrial life. Third, all seven planets may have liquid water, the key to life. But the probability of its presence is highest on the three planets that are closer to the star. Fourthly, if there really is life there, then we can confirm it without even sending a space expedition there. Telescopes like JWST, which is set to launch next year, will help answer this question.
We offer a selection of interesting scientific discoveries recent times.
See death. This month, British scientists managed to make interesting discovery: They captured on camera the process of death spreading. The process itself was a blue glow that literally permeated the cells of the body while it died. The very goal pursued by scientists from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council was to increase knowledge of the processes of death in order to further try to increase human life expectancy. (According to the Daily Mail. Photo: DailyMail)

Ancient Mayan temple. Last year, archaeologists discovered an ancient temple in the jungles of Guatemala. Presumably, this temple belonged to the Mayan tribes 1600 years ago and was called the “Temple of the Night Sun”. The temple itself is decorated with giant masks of the Mayan solar god.

New species of animals in Peru. Between 2009 and 2012, a group of biologists from Mexico and Peru went in search of new animal species to the northern part of Peru - the Tabaconas Namballe National Reserve. During the entire expedition they discovered many new species of mammals. Among them is an unknown species of night monkey. Only last year, scientists managed to agree that this species of monkey was truly unknown to science. Controversy still exists over some other mammal species. (according to nationalgeographic.com, photo: National Geographic)


Solar systems and planets. In April 2012, scientists discovered interesting star in the constellation South Hydra. The Sun-like star is located 127 light years from Earth. It is orbited by at least 9 planets, making it the largest solar system known. Our solar system has only 8 official planets. (according to nationalgeographic.com, photo: National Geographic)

Baby teeth and dictators. Scientists have made an interesting conclusion about why dictators are most likely born. Approximately 1 in 2,000 babies are born with one erupted tooth. For a mother, feeding such a child turns into real agony. The child feels a lack of attention, and with age he subconsciously tries to win it more and more. Anthropologists claim that people such as Julius Caesar, Hannibal, Napoleon, Mussolini and Hitler were born with an erupted tooth. (according to www.mentalfloss.com, photo: open sources)

Tie and vision. After many years of research, American scientists came to the conclusion that in 67% of men, vision impairment is associated with a tightly tightened collar. This especially applies to those who wear a tie. A tight tie restricts blood flow to the eyes. It also affects blood pressure. (according to Stephen Juan, “The odd body”, photo: open sources)


Chimpanzees and deceit. The conclusion was made by zoologists from Sweden. They discovered that a chimpanzee named Santino, who constantly threw stones at zoo visitors, prepared the crime weapon in advance. For a long time, Santino was under surveillance. Without showing any sign, he waited for the visitors to reach a certain place, and then quickly took out and threw a stone. Scientists have concluded that such an action is a consequence of a well-thought-out plan, which means chimpanzees are capable of deceit. (according to the journal PLoS ONE and the ScienceNOW website, photo: open sources )

Happiness and food. British scientists have come to the conclusion that only food can bring true happiness to a person. Everyone knows that a hungry person is often in a bad mood, but as soon as he eats, his mood improves. In first place among the “products of happiness” were all kinds of sweets and French fries - most people associate these products with relaxation. Next on the list is red and black caviar. She is associated with wealth and luxury. (according to www.geo.ru, photo: open sources)
![]()
Mars and water. NASA experts have come to the final conclusion that in the distant past there was water on the red planet suitable for living organisms. They were able to reach this conclusion using the Opportunity rover. Spacecraft found a piece of ancient clay that could only be formed in the presence of water. (according to bbc.co.uk, photo: NASA)

Science has always been and remains extremely important for the development of humanity and life in general, if only because thanks to science we can characterize, explore and, ultimately, understand the world in which we live, as well as find out how it works, how much it is Maybe. By increasing knowledge and understanding of the world (and beyond), we can identify and be more likely to protect endangered species, understand the origins of natural phenomena, treat diseases, determine the causes of climate change, and improve people's quality of life.
All this makes science perhaps the only discipline in which theories are confirmed through practical experiments. Some may even argue about the discipline's perspective, suggesting that science is an art - the art of discovery.
Thus, models can be developed that will allow scientists and engineers to create something new, help predict the consequences of events that could affect humanity, or even be able to predict the future. Although the importance of science in our daily lives is not always obvious, we actually make science-based choices countless times every day to help us improve or maintain our health and well-being.
The steady progress made in various fields of science means that scientists around the world are making new discoveries every day, and 2015 was no exception. Here are 25 of the most exciting scientific discoveries of the past year:
25. Computer program called "FaceDirector" generates the actor's emotions in the frame at the post-production stage, avoiding the need for re-shooting video
The research company Disney Research, together with scientists from the University of Surrey (UK), presented their brainchild called “FaceDirector” - a new method of synthesizing an actor’s facial expressions in a frame in post-production (the final stage of creating a film) to obtain the desired emotion, which avoids the need for repeated video recordings. In other words, soon actors won't have to try too hard to express their emotions - the computer will do everything for them.
24. Stem cell scientists have discovered a process that makes blood cells that challenges the conventional wisdom that has been held since the 1960s. 
Scientists at the University Health Network, Canada, studying stem cells have identified a completely new "two-level" process of blood cell formation, disproving an entire branch of physiology that scientific world adhered to for decades. The researchers say their discovery could revolutionize and open up opportunities for personalized treatment for people with blood disorders.
23. The destructive process has demonstrated potential in the treatment of cancer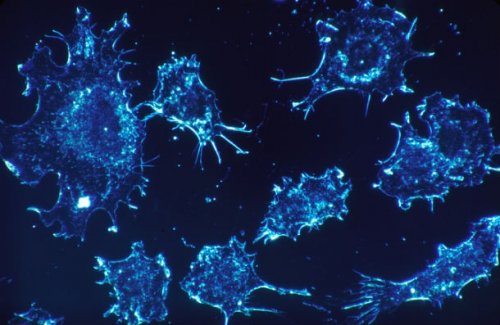
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in finding a new method of fighting cancer by attaching malaria proteins to cancer cells. They found that aggressive malaria proteins were able to attack cancer cells, showing 90% effectiveness. Clinical trials on humans are planned to begin within the next four years.
22. A new humanoid species discovered in South Africa 
Last September, paleontologists reported a new species of human ancestor, Homo naledi, based on 15 partial skeletons discovered in a remote cave called Dinaledi, the largest single discovery in Africa. It is believed that Homo naledi may have lived in Africa about 3 million years ago. Although researchers say the bones belong to a new species of human ancestor, other experts say much more evidence is needed to make such a claim.
21. Studies have shown that working more hours increases the risk of stroke.
According to research data published in the medical journal "The Lancet", people with a 55-hour working week The risk of suffering from a stroke is 33% higher than those who work 35 or 45 hours a week. In addition, they also have a 13% increased risk of developing coronary heart disease.
20. First comprehensive analyzes of the woolly mammoth genome completed
The first comprehensive analysis of the mammoth genome has revealed a number of features that allow these animals to adapt to life in the Arctic.
19. The WISE spacecraft discovered the most bright galaxy in the Universe
Last May, the infrared space telescope reported the discovery of the brightest galaxy, WISE J224607.57-052635.0. Smaller in size than Milky Way, this dusty galaxy releases 10,000 times more energy. Almost 100% of the light emitted by the galaxy is infrared radiation.
18. Scientists have achieved important steps towards creating the first real quantum computer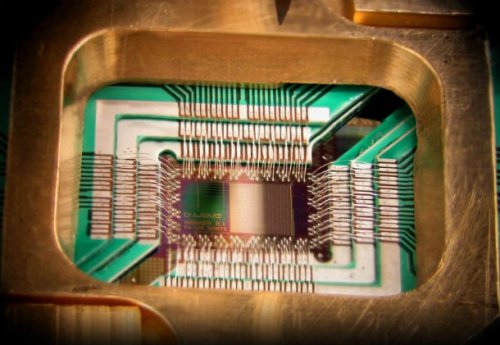
Two important steps towards creating a real computer based on quantum mechanics were achieved by scientists from IBM. They demonstrated a system capable of detecting and measuring both types of quantum errors simultaneously, and also developed a new circuit that is the only possible physical structure that can successfully scale to large sizes.
17. Small dinosaurs may have flown without feathers
Over the past two decades, Chinese scientists have repeatedly amazed the world scientific community with their discoveries in the field of paleontology, but last year’s discovery attracted the attention of even the most skeptical paleontologists. Last April, scientists reported the discovery of the remains of a dinosaur from the family Scansoriopterygidae in Hebei province, which they named Yi qi, which means “strange wing” in Chinese. According to scientists, he may have been able to fly without feathers. The body structure of this species is similar to terrestrial dinosaurs, but its wings resemble the structure of the wings of bats.
16. A Key Blood Pressure Medicine Revealed in Striking New Details
Research conducted at Arizona State University demonstrates the effects of an experimental blood pressure drug in unprecedented detail, potentially leading to the development of new, more effective drugs.
15. Visible spectrum of the first exoplanet
Astronomers have made the first direct detection of the spectrum of visible light reflected from an exoplanet. These observations also revealed new features of this object, the first exoplanet discovered around the star 51 Pegasi b. The results indicate great opportunities opening up in the field of observations, in particular associated with the advent of the next generation of receivers and telescopes of the future, such as, for example, E-ELT.
14. Physicists entangled 3 thousand atoms using one photon
Scientists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the University of Belgrade have developed new technology, which allows you to successfully entangle 3 thousand atoms at the quantum level using just one photon. The results, published in the journal Nature, demonstrate the largest number of particles ever entangled in an experiment or study.
13. Carbon sequestration in the Amazon is declining as trees are dying faster.
An impressive 30-year study of South American rain forests by the University of Leeds in England, involving an international team of 100 researchers, revealed disappointing results for our planet. The most extensive study ever has found that rain forests are gradually losing their ability to absorb carbon from the atmosphere as trees begin to die at a faster rate.
12. NASA discovered signs of a huge ancient ocean on Mars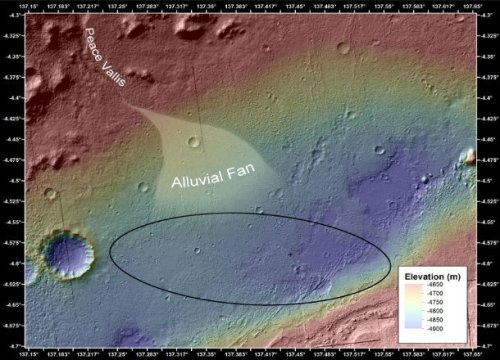
According to NASA scientists, an ancient ocean once covered almost half of Mars' northern hemisphere, making the planet a more promising place for alien life. A huge volume of water covered more than a fifth of the planet's surface, an area equal to the Atlantic Ocean, and in some places the depth of the ocean reached 1.6 kilometers. In total, the volume of the ocean was 20,000,000 km³ (larger in volume than the Arctic Ocean).
11. At the NASA Ames Research Center, the structure of the “building blocks of life” was reproduced in the laboratory.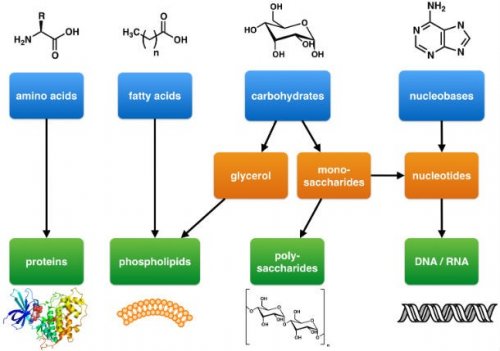
NASA scientists reported that in laboratory conditions simulating conditions outer space, for the first time, organic compounds that make up DNA and RNA - uracil, cytosine and thymine - were created. This was made possible by the use of pyrimidine, a chemical found in meteorites. According to scientists, pyrimidine (a heterocyclic compound with a characteristic odor that is the most carbon-rich chemical found in the Universe) may form in red giant stars or interstellar dust and gas clouds.
10. Is the Big Bang Theory refuted? The universe may not have had a beginning.
According to this theory (if it is confirmed), the Universe did not arise as a result of an explosion. A team of theoretical physicists from the University of Lethbridge (Canada) presented an alternative point of view, suggesting that the Universe has no beginning, is not a singularity, and that its age may be infinite. The new theory was outlined in a paper published on February 4, 2015 in the journal Physical Letters B.
9. Researchers have developed a nanomedicine to treat breast cancer
Iranian nanotechnologists have synthesized a nanopill design with a bioadaptive and biodegradable molecular chain that can attenuate the toxicity of anti-cancer drugs. It is believed that this modern drug can fight breast cancer much more effectively than any other, but only time can prove this.
8. Scientists have “reprogrammed” plants to make them drought-resistant.
Scientists have been able to genetically “reprogram” plants to be drought-resistant, avoiding the need for a new chemical that would have required years of testing to develop.
7. The world's first test tube baby from three parents becomes a reality
Last February, the UK government passed legislation allowing the use of controversial new three-parent IVF technology. The UK aims to become the first country in the world to offer this medical procedure. Proponents of the method argue that triparental IVF will allow women with genetic mutations mitochondria to give birth to your own healthy child, replacing the “sick” mitochondria with healthy mitochondria of another woman.
6. NASA's Kepler Space Telescope celebrated the discovery of its 1,000th exoplanet
Last January, NASA announced the confirmation of the thousandth exoplanet discovered by the Kepler space telescope. Three of the newly confirmed exoplanets were found orbiting within the habitable zone of their associated stars. Two of them, Kepler-438b and Kepler-442b, are similar in size to Earth and are likely rocky. The third exoplanet, Kepler-440b, is a super-Earth.
5. Scientists have compiled a genetic map of the bowhead whale
Scientists from the USA and Great Britain have deciphered the genome of the bowhead whale and identified the genes responsible for the longest life expectancy among mammals, reaching 200 years. The decoding of the genome, the result of two separate studies conducted in the US and UK, will allow scientists to identify a small number of genes responsible for cancer resistance, DNA repair and increased life expectancy.
4. New role of proteins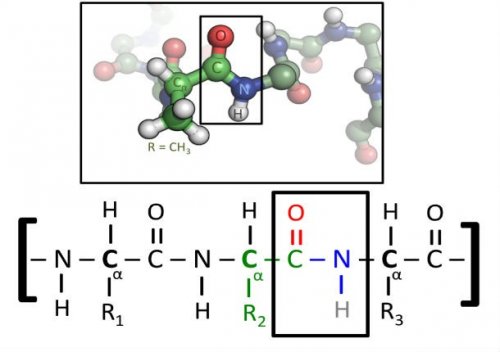
The study, published in the journal Science, shows evidence that a protein partially assembles another protein without using genetic instructions. Contrary to science textbooks, amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) can be assembled by another protein without genetic instructions.
3. Vaccine against HIV infection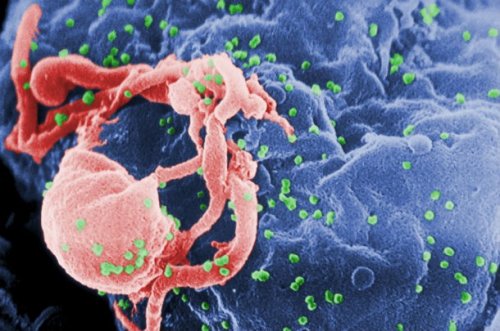
Scientists took a big step forward in the fight against HIV infection and AIDS last year when the Scripps Research Institute developed a vaccine that was highly effective against HIV-1, HIV-2 and African simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). The main difference is that the new HIV vaccine actually modifies DNA to fight the virus, rather than introducing a weakened form of it into the body, prompting the immune system to learn to fight it. Research is still in its early stages, and if it continues, treating HIV infection will become much easier.
2. Brain imaging can help predict future behavior
A review article published in the journal Neuron described a number of recent studies showing that brain scans (MRI) can help predict a person's future behavior, learning ability, criminality, health-related behavior, and response to medications or drugs. behavioral therapy. Technology can offer promise in personalizing educational and clinical practice.
1. Contracting human muscles were grown in laboratory conditions for the first time.
Researchers at Duke University (USA) have for the first time grown human skeletal muscles in the laboratory that contract and respond to external stimuli (such as electrical impulses, biochemical signals and drugs) in the same way as natural muscles. Tissue grown in the laboratory will allow scientists to test new drugs and study muscle diseases outside the human body.
