New scientific facts about the sun and stars. Interesting facts about the sun
Do you think you know everything about our luminary? We present to you interesting facts about the Sun. Some you probably already know, while others will be completely unexpected for you.
List of the most interesting facts
1. The Sun and the Solar System
We live on a planet and think that the Earth is an equal member solar system. The reality is that the mass of the central star is 99.8% of the mass of the Solar System. And most of the remaining 0.2% comes to Jupiter. Thus, the mass of the Earth is hundredths of the mass of the Solar System.
2. Our star is made mostly of hydrogen and helium
The sun is 74% hydrogen and 24% helium. The remaining 2% includes small amounts of iron, nickel, and oxygen. In other words, the solar system is mostly made of hydrogen.
3. The sun is very bright.
We know that there are surprisingly large and bright stars, such as Sirius and Betelgeuse. But they are incredibly far away. Our own star is a relatively bright star. If you could take the 50 closest stars within 17 light years of Earth, it would be the 4th brightest star.
4. The sun is huge, but at the same time tiny
Its diameter is 109 times larger than Earth's; 1,300 thousand Earths could fit inside it. But there are many big stars, whose diameter would almost reach the orbit of Saturn if the star were placed inside the Solar System.
5. Average age 4.5 billion years
Astronomers believe that our star formed about 4,590 million years ago. In about 5 billion years, it will enter the red giant stage and swell, then shed its outer layers and turn into a white dwarf.
6. The sun has a layered structure
Although our star looks like a burning fireball, it actually has an internal structure divided into layers. The visible surface, called the photosphere, is heated to a temperature of about 6000 degrees Kelvin. Below it is a convection zone, where heat slowly moves from the center to the surface, and cooled stellar matter falls down. This area starts at 70% of the radius. Below the convection zone is the radiation belt. In this zone, heat is transferred through radiation. The core extends from the center to a distance of 0.2 solar radii. This is a place where temperatures reach 13.6 million degrees Kelvin and hydrogen molecules fuse to form helium.
7. The sun can destroy all life on Earth
The sun is actually slowly warming up. It becomes 10% brighter every billion years. Within a billion years, the heat will be so intense that liquid water will not be able to exist on the surface of the Earth. Life on Earth will disappear forever. Bacteria will be able to live underground, but the surface of the planet will be scorched and uninhabitable. In 7 billion years it will become a red giant, and before it expands, the Sun will pull the Earth towards it and destroy the entire planet.
8. Its different parts rotate at different speeds
Unlike planets, the Sun is a huge sphere of hydrogen. Because of this, various parts rotate with at different speeds. You can see how fast a surface is rotating by tracking the movement of spots across the surface. A rotation at the equator takes 25 days, while at the poles, a complete rotation can take 36 days.
9. The outer atmosphere is hotter than its surface
The surface has a temperature of 6000 degrees Kelvin. But this is much less than the temperature of the star's atmosphere. Above the surface there is a region of the atmosphere called the chromosphere, its temperature can reach 100,000 K. Even more distant regions, called the corona, reach temperatures of 1 million K.
10. There are spacecraft studying it right now.
The most famous spaceship, sent to observe, launched in December 1995 and called SOHO. SOHO constantly monitors our star. In 2006, two devices of the STEREO mission were launched. The two spacecraft were designed to view activity from two different perspectives, providing 3D models of our star and allowing astronomers to more accurately predict space weather.
The Sun is the “heart” of the Solar System, and planets and satellites revolve around it. Scientists argue that it is enough to even slightly change the mass of the sun or its size, and life on our planet simply would not exist.
I have prepared a selection of very interesting facts about the only star in the solar system.
1. The sun is really big
In fact, the Sun makes up more than 99.8% of the total mass of the Solar System. This is not a mistake - all planets, their moons and all other small space objects make up less than 0.2% of the mass of the Solar System. To be more precise, the mass of the Sun is about two nonillion kilograms (that's two point thirty zeros). The volume of the Sun is approximately 1.3 million planets, equal to Earth.
In fact, the mass of the Sun is quite often used in astronomy as a standard unit of measurement for large objects. When it comes to stars, nebulae, or even galaxies, astronomers often use the comparison to the Sun to describe their mass.
2. On a galactic scale, the Sun is not particularly large

Although we were just talking about the fact that the Sun is indeed very large, but this is only in comparison with other objects in the solar system. There are much more massive things in the Universe. The Sun is classified as a G-type star, which is generally called a yellow dwarf.
As the name suggests, there are much larger stars, classified as giants, supergiants and hypergiants. The red supergiant Uy Scuti is located 9,500 light-years from Earth. This is currently the largest famous star with a diameter approximately 1700 times greater than that of the Sun. Its circumference is 7.5 billion kilometers. Even light takes almost seven hours to circle a star. If Uy Scuti were in the Solar System, then the surface of the star would extend beyond the orbit of Jupiter.
3. What happens when the Sun dies
Stars can live for a very long time, billions of years, but eventually they too die. The further fate of stars depends on their size. The remains of smaller stars turn into so-called brown dwarfs. Massive stars die more violently - they go supernova or even hypernova and collapse into neutron star or a black hole. In rare cases, these giants can even explode, followed by a gamma-ray burst.
The sun is somewhere in the middle - it will not explode, but it will not “deflate” either. Once the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it will begin to collapse in on itself under its own weight, causing the core to become denser and hotter. This will cause the Sun to expand and become a red giant. Eventually, it will collapse into a white dwarf - a tiny stellar remnant of incredible density (about the size of the Earth, but the mass of the Sun).
4. What does the Sun consist of?
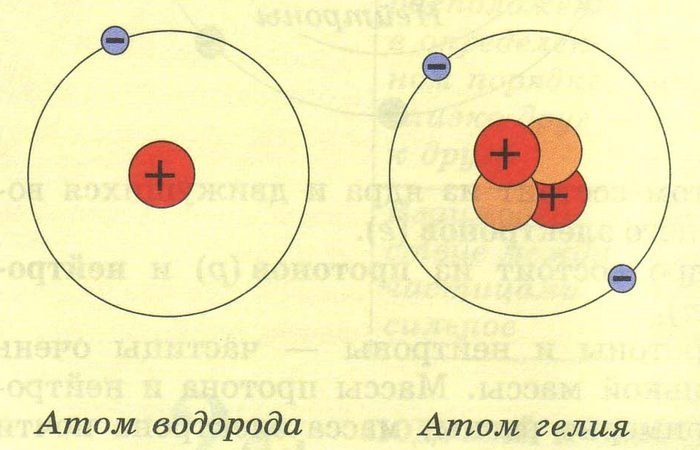
It is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, like most stars. To be more precise, it is about 71% hydrogen, 27% helium, and the remaining 2% comes from trace amounts of dozens of chemical elements, mainly oxygen and carbon.
5. How hot is the Sun?

The temperature of the Sun really depends on what part of the Sun we are talking about. The core of the Sun is insanely hot - temperatures there reach 15 million degrees Celsius. In the chromosphere, the temperature is “only” a few thousand degrees. However, temperatures quickly rise to millions of degrees in the Sun's outer layer, the corona. Why this is so, scientists do not know for sure.
6. How old is the Sun
The age of the Sun is about 4.6 billion years. Its age was calculated based on the ages of other things in the solar system that can be dated more precisely, such as meteorites or even rocks on Earth. Naturally, this is true under the assumption that the solar system formed as a single whole. The lifespan of a G-type star is from 9 to 10 billion years.
7. How bright is the Sun
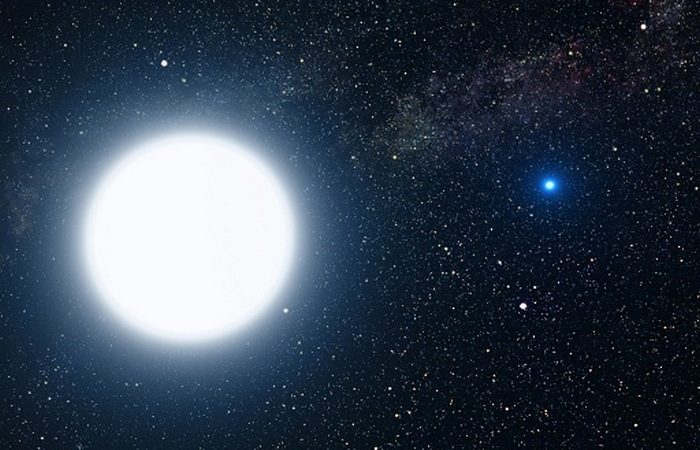

Sirius A is gigantic, huh bright Star Sirius B (right) is much smaller in size. Obviously, the Sun is the brightest in the daytime sky because it is much closer to Earth than any other star. In the night sky, the brightest star is Sirius. The second brightest is Canopus.
Apparent magnitude is the term used to indicate the brightness of a celestial object from Earth. The Sun has an apparent magnitude of -27.
8. How fast the sun rotates

The rotation of the Sun is a little difficult to calculate as it varies depending on the region. To put it briefly, without explanation, the Sun makes a full revolution in about 25.4 days. The sun doesn't actually rotate as a rigid body like the Earth. It rotates fastest at the equator (24.5 days) and slowest near the poles (38 days).
Regarding the speed of the Sun in the Universe, the entire Solar System orbits around the center Milky Way at a speed of 828,000 km/h. One complete revolution, known as a galactic year, takes approximately 225 - 250 million Earth years.
9. What are sunspots?
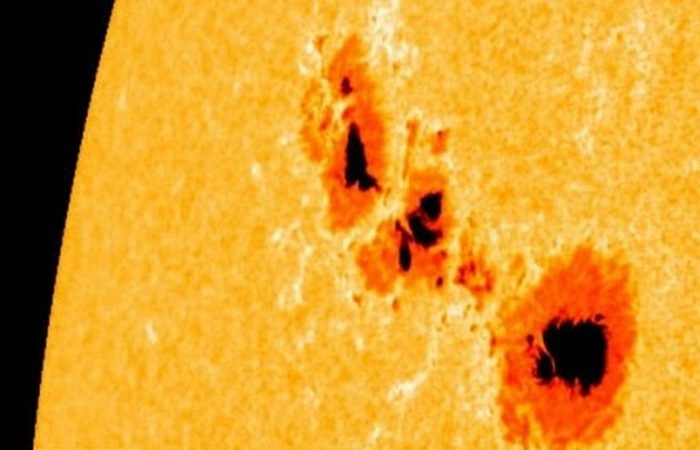

Dark spots known as sunspots can sometimes be observed on the surface of the Sun. They have a lower temperature (by about 1,226 degrees Celsius) than the rest of the solar surface and are caused by fluctuations in the Sun's magnetic field. Some may be large enough to be seen with the naked eye. Sometimes groups of more than 100 sunspots appear simultaneously. However, this happens extremely rarely.
10. The sun changes its magnetic field
Every 11 years, the South and North magnetic poles change places. This also happens on Earth, but much less frequently. IN last time this happened about 800,000 years ago.
It seems that we know everything about the Sun, because many scientific works have been written about it and many hypotheses have been expressed. But perhaps the most interesting 10 facts about the hottest planet presented by our portal are still unknown to anyone.
The Sun is the main planet of the Solar System. To those living on Earth, it seems that for the most part it is the same as all the other planets of the Solar System. However, this is not quite true. Only 0.2 percent of the solar system's total mass comes from its planets. The remaining 99.8 percent is from the Sun. Of all the planets, the planet has the largest mass Jupiter
The composition of the Sun is hydrogen and helium
What is the mass of the Sun itself? It turns out that 74% is hydrogen, 24% is helium. And only 2 percent of the total mass consists of elements such as iron, magnesium, nickel, zinc, oxygen and other chemical elements present in the system.
The sun is bright
Despite its brightness, the Sun has only
fourth place, if we consider it among the fifty brightest planets located from Earth at a distance of seventeen light years. Brighter than the Sun many times, the huge planet Carina, as well as Betelgeuse. Thus, the brightness of our Sun is very relative.
The sun is huge, but...
The enormous size of our Sun is amazing when you imagine that 1.3 million planets the size of our Earth can be placed inside it. And if we imagine that our planet has become flat and measure its area, and then place it on the surface of the Sun, then to completely cover its surface, 11,900 such planets would be needed.
Age of our Sun
4.59 billion years have passed since the formation of our Solar System (Sun and planets). The Sun is currently beginning to slowly fade, consuming its own fuel, which is hydrogen, while in its main sequence stage. The Sun is about 5 billion years away from the phase called the red giant. After that, it will absorb the system, including our Earth. Then, having shed its outer layered shell, it will shrink and acquire the size of a very tiny planet called a white dwarf.
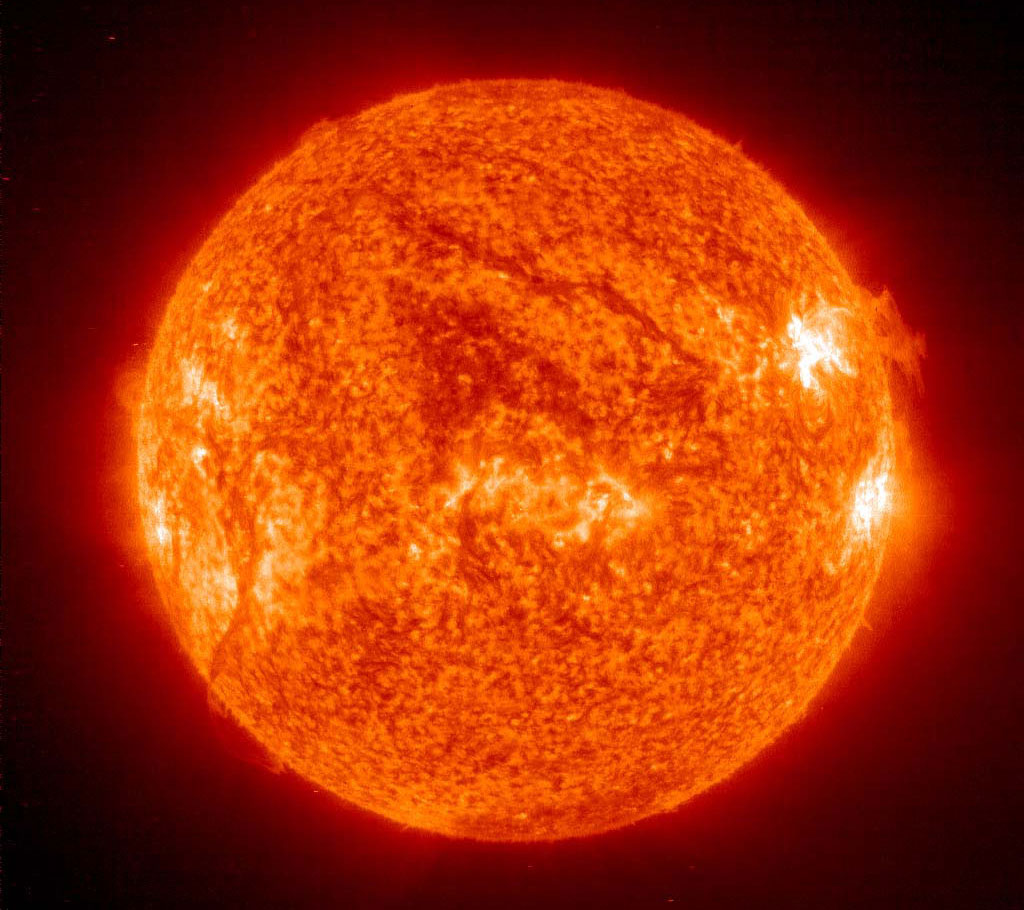 Solar structure
Solar structure
The Sun, which looks like a brightly burning ball, is at the same time a planet that has its own internal unusual structure. Its surface visible from Earth, called the photosphere by scientists, heats up to six thousand degrees Kelvin. Inside the Sun there is a core whose size is equal to 0.2 of its radius. The temperature inside the core is about 13.6 degrees. At this temperature, helium is formed from hydrogen molecules. The zone where the plasma is formed is called the radiative zone and is located below the convective zone, located at a distance of approximately 0.7 radii of the Sun itself. In this zone, located under the photosphere, plasma slowly advances from the depths, cooling, falling in columns.
The sun can kill...
The temperature on the surface of our Sun is gradually increasing. Each subsequent billion years it increases by 10 percent. The intensity of radiation will increase every billion years to such an extent that all life on Earth will disappear, and it will become uninhabitable, since water will disappear from our planet, although bacteria will survive underground. The Sun will reach the stage of a red giant in several billion years, more precisely in 7, and will expand, consuming our Earth with the planets existing in the system.
Rotation of parts of the Sun The sun has the appearance of a huge sphere containing hydrogen, the various parts having rotating speeds. If you look at sunspots, you will notice their rapid movement, which indicates the rapid rotation of the sun's surface. It is noted that the equatorial zones have a rotation of 25 days, and the pole zones - 36. According to scientists, 27 days is the speed at which rotation occurs inside the Sun itself.
The surface of the Sun is cooler than the atmosphere
Six thousand degrees of surface temperature is colder than the atmosphere itself. The part of the atmosphere above solar surface is called the chromosphere, the temperature of which can be equal to 100,000 degrees Kelvin. In addition, there is an area above the Sun called the corona. Located at a great distance from the Sun, larger in size than the star itself, it can have a temperature of about a million degrees.
