The nearest neighboring star is named. The stars closest to us
Since ancient times, man has turned his gaze to the sky, where he saw thousands of stars. They fascinated him and made him think. Over the centuries, knowledge about them accumulated and systematized. And when it became clear that the stars are not just luminous points, but real cosmic objects of enormous size, a person had a dream - to fly to them. But first we had to determine how far away they were.
The closest star to Earth
Using telescopes and mathematical formulas scientists managed to calculate the distances to ours (excluding objects solar system) space neighbors. So, which star is closest to Earth? It turned out to be little Proxima Centauri. It is part of a triple system located at a distance of approximately just over four light years from the Solar System (it is worth noting that astronomers more often use another unit of measurement - the parsec). She was named proxima, which means “nearest” in Latin. For the Universe, this distance seems insignificant, but with the current level of space shipbuilding, it will take more than one generation of people to reach it.
Proxima Centauri
In the sky this star can only be seen through a telescope. It shines about one hundred and fifty times weaker than the Sun. It is also significantly smaller in size than the latter, and its surface temperature is two times lower. Astronomers consider this star and the existence of planets around it to be unlikely. And therefore there is no point in flying there. Although the triple system itself deserves attention - such objects are not very common in the Universe. The stars in them revolve around one another in bizarre orbits, and sometimes they “devour” their neighbor.
Deep space
Let's say a few words about the most distant of those discovered on this moment object in the Universe. Of those visible without the use of special optical devices, this is, without a doubt, the Andromeda Nebula. Its brightness is approximately a quarter magnitude. And the most nearby star to the Earth of this galaxy is located from us, according to astronomers, at a distance of two million light years. Mind-blowing magnitude! After all, we see it as it was two million years ago - that’s how easy it is to look into the past! But let's return to our “neighbors”. The closest galaxy to us is a dwarf galaxy, which can be observed in the constellation Sagittarius. She is so close to us that she practically absorbs her! True, it will still take eighty thousand light years to fly to it. These are the distances in space! The Magellanic Cloud is not worth talking about. This satellite Milky Way is almost 170 million light years behind us.

The closest stars to Earth
There are fifty-one relatively close to the Sun. But we will list only eight. So, meet:
- Proxima Centauri, already mentioned above. Distance - four light years, class M5.5 (red or brown dwarf).
- The stars Alpha Centauri A and B. They are 4.3 light years away from us. Objects of class D2 and K1 respectively. Alpha Centauri is also the closest star to Earth, similar in temperature to our Sun.
- Barnard's Star - it is also called “Flying” because it moves at a high speed (compared to other space objects). Located at a distance of 6 light years from the Sun. Object class M3.8. In the sky it can be found in the constellation Ophiuchus.
- Wolf 359 is located 7.7 light years away. 16th magnitude object in the constellation Draco. Class M5.8.
- Lalande 1185 is 8.2 light years away from our system. Located in Object class M2.1. Magnitude - 10.
- Tau Ceti is located 8.4 light years away. M5,6 class star.
- The Sirius A and B system is eight and a half light years away. Stars class A1 and DA.
- Ross 154 in the constellation Sagittarius. Located at a distance of 9.4 light years from the Sun. M class star 3.6.
Only space objects located within a radius of ten light years from us are mentioned here.

Sun
However, looking at the sky, we forget that the closest star to Earth is still the Sun. This is the center of our system. Without it, life on Earth would have been impossible, and our planet was formed along with this star. That's why she deserves special attention. A little about her. Like all stars, the Sun is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. Moreover, the first constantly turns into the last. As a result, heavier elements are also formed. And the older the star, the more they accumulate.
In terms of age, the closest star to Earth is no longer young, it is about five billion years old. is ~2.10 33 g, diameter - 1,392,000 kilometers. The temperature on the surface reaches 6000 K. In the middle of the star it rises. The atmosphere of the Sun consists of three parts: the corona, the chromosphere and the photosphere. 
Solar activity significantly affects life on Earth. It is argued that climate, weather and the state of the biosphere depend on it. It is known about the eleven-year periodicity of solar activity.
>The closest star to the Sun
To catch your friends, you can ask them about closest star. Most people immediately start talking about Betelgeuse or Sirius. But here lies the catch. Of course, the Sun is closest to the Earth (150 million km). But which one is closer to it?
Who is closest?
Alpha Centauri ranks third in brightness and lives only 4.37 light years away. But this is not a single object, but a triple system. First of all, we see a binary pair orbiting general center gravity for 80 years. A is brighter, and B is slightly inferior. The third member is Proxima Centauri. Remember this name, since it ranks first in terms of proximity to our system (4.24 light years).
The system covers an area in the constellation Centaurus, which can only be seen from the southern hemisphere. But even there you won’t be able to see this star. The fact is that it is too weak and you will need powerful equipment. To give you an idea, it would have taken New Horizons 78,000 years to get to Proxima Centauri.
It has been in first place in terms of proximity for 32,000 years and will remain in this position for another 33,000 years. In 26,700 years it will reduce the distance to 3.11 light years. After it, Ross 248 will come closest.
What about the northern hemisphere?
Here the closest one will be Barnard's star - a red dwarf (). But it is also dim and not visible to the naked eye. If we take only those that can be observed without technology, then the closest one is located (8.6 light years). It is twice the size and mass of the Sun.

How are distances to stars measured?
Parallax is used for this. What's the point? Extend your arm and place your finger in front of a distant object. Close your eyes one at a time and you will understand that the object seems to be moving. This is parallax.
It is necessary to calculate the distance to the star when our planet is in one of the orbits (in summer), and then wait 6 months until it is on the opposite side and measure again. Then we measure the angle in relation to another object. This scheme works for any object living within 100 light years.
| Star system | Star or brown dwarf | Spec. Class | View. sound led | Distance, St. year |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | solar system | Sun | 0 | G2V | −26.72 ± 0.04 | 8.32 ± 0.16 light min |
| 1 | α Centauri | 1 | M5.5Ve | 11,09 | 4.2421 ± 0.0016 | |
| α Centauri A | 2 | G2V | 0,01 | 4.3650 ± 0.0068 | ||
| α Centauri B | 2 | K1V | 1,34 | |||
| 2 | 4 | M4Ve | 9,53 | 5.9630 ± 0.0109 | ||
| 3 | Luhmann 16 | A | 5 | L8 | 23,25 | 6.588 ± 0.062 |
| B | 5 | L9/T1 | 24,07 | |||
| 4 | WISE 0855–0714 | 7 | Y | 13,44 | 7,18 +0,78 −0,65 | |
| 5 | Wolf 359 | 8 | M6V | 13,44 | 7.7825 ± 0.0390 | |
| 6 | Lalande 21185 | 9 | M2V | 7,47 | 8.2905 ± 0.0148 | |
| 7 | Sirius | Sirius A | 10 | A1V | −1,43 | 8.5828 ± 0.0289 |
| Sirius B | 10 | DA2 | 8,44 | |||
| 8 | Leithen 726-8 | Leithen 726-8 A | 12 | M5.5Ve | 12,54 | 8.7280 ± 0.0631 |
| Leithen 726-8 B | 12 | M6Ve | 12,99 | |||
| 9 | Ross 154 | 14 | M3.5Ve | 10,43 | 9.6813 ± 0.0512 | |
| 10 | Ross 248 | 15 | M5.5Ve | 12,29 | 10.322 ± 0.036 | |
| 11 | WISE 1506+7027 | 16 | T6 | 14.32 | 10,521 | |
| 12 | ε Eridani | 17 | K2V | 3,73 | 10.522 ± 0.027 | |
| 13 | Lacaille 9352 | 18 | M1.5Ve | 7,34 | 10.742 ± 0.031 | |
| 14 | Ross 128 | 19 | M4Vn | 11,13 | 10.919 ± 0.049 | |
| 15 | WISE 0350-5658 | 20 | Y1 | 22.8 | 11,208 | |
| 16 | EZ Aquarius | EZ Aquarius A | 21 | M5Ve | 13,33 | 11.266 ± 0.171 |
| EZ Aquarius B | 21 | M? | 13,27 | |||
| EZ Aquarius C | 21 | M? | 14,03 | |||
| 17 | Procyon | Procyon A | 24 | F5V-IV | 0,38 | 11.402 ± 0.032 |
| Procyon B | 24 | D.A. | 10,70 | |||
| 18 | 61 Swans | 61 Cygnus A | 26 | K5V | 5,21 | 11.403 ± 0.022 |
| 61 Cygnus B | 26 | K7V | 6,03 | |||
| 19 | Struve 2398 | Struve 2398 A | 28 | M3V | 8,90 | 11.525 ± 0.069 |
| Struve 2398 B | 28 | M3.5V | 9,69 | |||
| 20 | Groombridge 34 | Groombridge 34 A | 30 | M1.5V | 8,08 | 11.624 ± 0.039 |
| Groombridge 34 B | 30 | M3.5V | 11,06 | |||
| 21 | ε Indian | ε Indian A | 32 | K5Ve | 4,69 | 11.824 ± 0.030 |
| ε Indian B | 32 | T1V | >23 | |||
| ε Indian C | 32 | T6V | >23 | |||
| 22 | DX Cancer | 35 | M6.5Ve | 14,78 | 11.826 ± 0.129 | |
| 23 | τ China | 36 | G8Vp | 3,49 | 11.887 ± 0.033 | |
| 24 | GJ 1061 | 37 | M5.5V | 13,09 | 11.991 ± 0.057 | |
| 25 | YZ China | 38 | M4.5V | 12,02 | 12.132 ± 0.133 | |
| 26 | Leithen's Star | 39 | M3.5Vn | 9,86 | 12.366 ± 0.059 | |
| 27 | Teagarden's Star | 40 | M6.5V | 15,14 | 12.514 ± 0.129 | |
| 28 | SCR 1845-6357 | SCR 1845-6357 A | 41 | M8.5V | 17,39 | 12.571 ± 0.054 |
| SCR 1845-6357 B | 42 | T6 | ||||
| 29 | Kapteyn's Star | 43 | M1.5V | 8,84 | 12.777 ± 0.043 | |
| 30 | Lacaille 8760 | 44 | M0V | 6,67 | 12.870 ± 0.057 | |
| 31 | WISE J053516.80-750024.9 | 45 | Y1 | 21,1 | 13,046 | |
| 32 | Kruger 60 | Kruger 60 A | 46 | M3V | 9,79 | 13.149 ± 0.074 |
| Kruger 60 B | 46 | M4V | 11,41 | |||
| 33 | DEN 1048-3956 | 48 | M8.5V | 17,39 | 13.167 ± 0.082 | |
| 34 | UGPS J072227.51-054031.2 | 49 | T9 | 24.32 | 13,259 | |
| 35 | Ross 614 | Ross 614 A | 50 | M4.5V | 11,15 | 13.349 ± 0.110 |
| Ross 614 B | 50 | M5.5V | 14,23 | |||
| 37 | Wolf 1061 | 53 | M3V | 10,07 | 13.820 ± 0.098 | |
| 38 | Van Maanen's Star | 54 | DZ7 | 12,38 | 14.066 ± 0.109 | |
| № | Designation | Designation | № | Spec. Class | View. sound led | Distance, St. year |
| Star system | Star or brown dwarf | |||||
There are 45 stars located at a distance of 17 light years from the system. There may be 200 billion in total in the galaxy. Some are so weak that they cannot be detected.
Which star is closest to Earth? Most will immediately remember Alpha Centauri, Sirius, or even the North Star.
And only then will they realize that closest star to Earth- this is the Sun:-)
Okay, then what is the name of the closest star to the Sun?
For a long time it was believed that the closest star to the Sun is Alpha Centauri, which is located in the southern hemisphere of the sky. The distance to it is 4.37 light years. But, in 1915, the star Proxima Centauri was discovered near Alpha Centauri, which most likely belongs to the Alpha Centauri system.
Therefore, in general we can say that the Alpha Centauri system is the closest star system to Earth, meaning all its components.
Read more below.
The closest star to Earth
The most big star in the Alpha Centauri system it is the star Alpha Centauri A.
Nearby is a second star - Alpha Centauri B, somewhat smaller in size.
Both of these stars revolve around a common center of mass and therefore they can alternately become the closest star to Earth.
But around this pair of Alpha Centauri stars another tiny star revolves - the red dwarf Proxima Centauri.
The trajectories of these three stars relative to each other are quite complex.
And yet, at present it is Proxima Centauri that is the closest star to Earth.
Proxima Centauri
The star Proxima Centauri is a red dwarf, its apparent magnitude is only 11.05 m. The absolute magnitude is only 15.49 m.
Therefore, even being on Alpha Centauri, we can see Proxima Centauri as a dim star of approximately 5th magnitude.
The distance from the Sun to Proxima Centauri is 4.22 light years.
There are suggestions that Proxima Centauri orbits the Alpha Centauri system with a period of about 500,000 years. Therefore, Proxima Centauri is sometimes also called Alpha Centauri C, that is, it is considered the third element star system Alpha Centauri.
The orbital radius of Proxima Centauri around Alpha Centauri is about 15,000 ± 700 AU. e. or about 0.21 light years. For comparison, the distance from Proxima Centauri to the Sun is only 20 times greater than this value.
The belonging of Proxima Centauri to the system is considered not fully proven. However, this assumption is supported by the fact that the vectors of proper motions of Proxima Centauri and separately the Alpha Centauri pair almost coincide. And identical motion vectors are inherent precisely in stars that are part of the same system.
Using the Hubble telescope, the space around Proxima Centauri was explored and it was found that there are no red dwarfs in its orbit. There are also no super-Earths (planets slightly larger than Earth) in the habitable belt.
However, on August 24, 2016, the European Southern Observatory confirmed the existence of an Earth-like planet in the habitable zone of Proxima Centauri. The planet was named Proxima Centauri b.
Whether life is possible on the planet Proxima Centauri b is a controversial issue.
Yes, the planet is in the habitable belt, and this is already a great success, since the habitable belt around such a small star is very narrow.
But, Proxima Centauri is a periodically flaring star. During these flares, the level of not only ordinary, but also x-ray radiation increases sharply. And this is already extremely undesirable for living beings (by analogy with protein life on Earth).
The closest stars to Earth in the past and future
The stars do not stand still, they move, although this is not noticeable even throughout the life of one person. Has Proxima Centauri always been the closest star to the Sun and how long will it remain so?
Proxima Centauri has been the closest star to the Sun for the past 32,000 years and will remain so for a long time to come. And in 33,000 years, the closest star to the Sun will be Ross 248, a single star from the constellation Andromeda. The star Ross 248 is now 10.3 light-years from the Sun—that's 2.5 times farther than the distance to Proxima Centauri today.
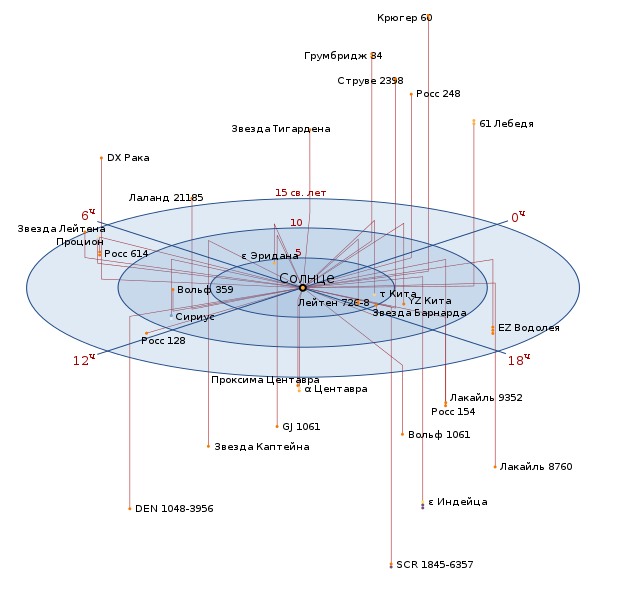
List of closest stars to Earth
Here you can look at list of stars closest to Earth and find out their main characteristics.
After the table, a spatial map of the relative positions of these stars relative to the Sun is given.
| № | Star system | Star | Range. Class | View. sound led | Abs. sound led | Coordinates (J2000.0 era) |
Distance, St. year |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct sunrise | Slope. | |||||||
| 0 | solar system | Sun | G2V | −26.72 ± 0.04 | 4,83 | change as the Sun moves along the ecliptic | 8.32 ± 0.16 light min | |
| 1 | α Centauri | Proxima Centauri | M5.5Ve | 11,09 | 15,53 | 14 h 29 m 43.0 s | −62° 40′ 46″ | 4.2421 ± 0.0016 |
| A | G2V | 0,01 | 4,38 | 14 h 39 m 36.5 s | −60° 50′ 02″ | 4.3650 ± 0.0068 | ||
| B | 1,34 | 5,71 | 14 h 39 m 35.1 s | −60° 50′ 14″ | ||||
| 2 | Barnard's Star | M4Ve | 9,53 | 13,22 | 17 h 57 m 48.5 s | +04° 41′ 36″ | 5.9630 ± 0.0109 | |
| 3 | Luhmann 16 | A | L8 | 23,25 | 10h 49m 15.57s | −53° 19′ 06″ | 6.588 ± 0.062 | |
| B | L9/T1 | 24,07 | ||||||
| 4 | WISE 0855–0714 | Y | 08h 55m 11s | −07° 14′ 43″ | 7,18 +0,78 −0,65 | |||
| 5 | Wolf 359 | M6V | 13,44 | 16,55 | 10 h 56 m 29.2 s | +07° 00′ 53″ | 7.7825 ± 0.0390 | |
| 6 | Lalande 21185 | M2V | 7,47 | 10,44 | 11h 03m 20.1s | +35° 58′ 12″ | 8.2905 ± 0.0148 | |
| 7 | Sirius | A | A1V | −1,43 | 1,47 | 06h 45m 08.9s | −16° 42′ 58″ | 8.5828 ± 0.0289 |
| B | DA2 | 8,44 | 11,34 | |||||
| 8 | Leithen 726-8 | A | M5.5Ve | 12,54 | 15,40 | 01h 39m 01.3s | −17° 57′ 01″ | 8.7280 ± 0.0631 |
| B | M6Ve | 12,99 | 15,85 | |||||
| 9 | Ross 154 | M3.5Ve | 10,43 | 13,07 | 18 h 49 m 49.4 s | +23° 50′ 10″ | 9.6813 ± 0.0512 | |
| 10 | Ross 248 | M5.5Ve | 12,29 | 14,79 | 23 h 41 m 54.7 s | +44° 10′ 30″ | 10.322 ± 0.036 | |
| 11 | WISE 1506+7027 | T6 | 15h 06m 49.9s | +70° 27′ 36″ | 10,521 | |||
| 12 | ε Eridani | K2V | 3,73 | 6,19 | 03h 32m 55.8s | −09° 27′ 30″ | 10.522 ± 0.027 | |
| 13 | Lacaille 9352 | M1.5Ve | 7,34 | 9,75 | 23 h 05 m 52.0 s | −35° 51′ 11″ | 10.742 ± 0.031 | |
| 14 | Ross 128 | M4Vn | 11,13 | 13,51 | 11h 47m 44.4s | +00° 48′ 16″ | 10.919 ± 0.049 | |
| 15 | WISE 0350-5658 | Y1 | 03 h 50 m 00.32 s | −56° 58′ 30.2″ | 11,208 | |||
| 16 | EZ Aquarius | A | M5Ve | 13,33 | 15,64 | 22 h 38 m 33.4 s | -15° 18′ 07″ | 11.266 ± 0.171 |
| B | M? | 13,27 | 15,58 | |||||
| C | M? | 14,03 | 16,34 | |||||
| 17 | Procyon | A | F5V-IV | 0,38 | 2,66 | 07h 39m 18.1s | +05° 13′ 30″ | 11.402 ± 0.032 |
| B | D.A. | 10,70 | 12,98 | |||||
| 18 | 61 Swans | A | K5V | 5,21 | 7,49 | 21h 06m 53.9s | +38° 44′ 58″ | 11.403 ± 0.022 |
| B | K7V | 6,03 | 8,31 | 21h 06m 55.3s | +38° 44′ 31″ | |||
| 19 | Struve 2398 | A | M3V | 8,90 | 11,16 | 18 h 42 m 46.7 s | +59° 37′ 49″ | 11.525 ± 0.069 |
| B | M3.5V | 9,69 | 11,95 | 18 h 42 m 46.9 s | +59° 37′ 37″ | |||
| 20 | Groombridge 34 | A | M1.5V | 8,08 | 10,32 | 00 h 18 m 22.9 s | +44° 01′ 23″ | 11.624 ± 0.039 |
| B | M3.5V | 11,06 | 13,30 | |||||
| 21 | ε Indian | A | K5Ve | 4,69 | 6,89 | 22h 03m 21.7s | −56° 47′ 10″ | 11.824 ± 0.030 |
| B | T1V | >23 | >25 | 22h 04m 10.5s | −56° 46′ 58″ | |||
| C | T6V | >23 | >25 | |||||
| 22 | DX Cancer | M6.5Ve | 14,78 | 16,98 | 08h 29m 49.5s | +26° 46′ 37″ | 11.826 ± 0.129 | |
| 23 | τ China | G8Vp | 3,49 | 5,68 | 01h 44m 04.1s | −15° 56′ 15″ | 11.887 ± 0.033 | |
| 24 | GJ 1061 | M5.5V | 13,09 | 15,26 | 03h 35m 59.7s | −44° 30′ 45″ | 11.991 ± 0.057 | |
| 25 | YZ China | M4.5V | 12,02 | 14,17 | 01h 12m 30.6s | −16° 59′ 56″ | 12.132 ± 0.133 | |
| 26 | Leithen's Star | M3.5Vn | 9,86 | 11,97 | 07h 27m 24.5s | +05° 13′ 33″ | 12.366 ± 0.059 | |
| 27 | Teagarden's Star | M6.5V | 15,14 | 17,22 | 02 h 53 m 00.9 s | +16° 52′ 53″ | 12.514 ± 0.129 | |
| 28 | SCR 1845-6357 | A | M8.5V | 17,39 | 19,41 | 18 h 45 m 05.3 s | −63° 57′ 48″ | 12.571 ± 0.054 |
| B | T6 | 18 h 45 m 02.6 s | −63° 57′ 52″ | |||||
| 29 | Kapteyn's Star | M1.5V | 8,84 | 10,87 | 05h 11m 40.6s | −45° 01′ 06″ | 12.777 ± 0.043 | |
| 30 | Lacaille 8760 | M0V | 6,67 | 8,69 | 21 h 17 m 15.3 s | −38° 52′ 03″ | 12.870 ± 0.057 | |
 Did you like it? Tell your friends:
Did you like it? Tell your friends: Everyone can tell which star is closest to Earth, but not everyone knows additional information about it.
This star is a type of yellow dwarf. And it appeared as much as 5 billion years ago. The light emitted by the Sun reaches the Earth in just 8 minutes at such a huge distance as approximately 150 million kilometers (this number is taken as 1 astronomical unit). This is the center of all planetary systems: 8 planets with satellites, many comets and meteorites revolve around it.
The mass of this star exceeds the mass of the Earth by about 330 thousand times, and its size is 109 times greater! For clarity, you can look at the video below, which clearly shows the scale of the planets with the Sun.
The sun is the brightest object in the entire earth's sky. Thanks to the energy generated by the sun, life originated on Earth. Interestingly, it consists of only 90% hydrogen and 10% helium. The composition, of course, includes other substances, but their percentage is only 0.1%
First studies
Once upon a time, people thought that the Sun was not a moving object. Galileo Galilei destroyed this idea, because in 1610 he saw the movement of spots on the surface with the help of his telescope. Based on this, it was concluded that it was rotating. And it rotates, by the way, not like a solid body: in the region of the equator, the period of rotation around its axis is 25 days, and the period of rotation around the poles reaches 30 days. Rotating at a speed of about 200 -220 kilometers per second, it will take approximately 200 million years to complete a revolution around the center of the galaxy.
The sun and life on Earth
This star releases simply a huge amount of energy, or to be more precise, 6.5 kW from one square centimeter of surface. This energy, by the way, remains unchanged throughout the life of the Sun. Interestingly, only a billionth of this energy will be enough for life on Earth. If the energy that would be transferred to our planet changed up or down, life on Earth would most likely cease.

According to scientific calculations by scientists, the Sun will not live forever: it will exist for about 5 billion more years, after which it will heat up and increase in size. Thanks to such changes, the conditions of life on Earth will change and the time will come when these conditions will become completely unbearable for life on the planet.
In order to determine the deserved place of our Sun among the stars, let's first look at its neighbors. The Sun's closest neighbor is a system of three stars orbiting one another. The brightest of them Alpha Centauri A, - this is very similar to our yellow Sun. Alpha Centauri B slightly smaller, and its light has an orange tint, since its surface temperature is cooler - about 4800 ° C, while the temperature of the Sun reaches 5800 ° C. tells us about its temperature. Cool stars are red, hotter ones are orange, yellow and bluish-white.
The orbital period of the two main stars of the Alpha Centauri system relative to each other is about 80 years. They are located quite far from each other (the distance between them is comparable to the distance from the Earth to the Sun or from the Sun to the planet Uranus). The third star in the system Alpha Centauri - C, or Proxima Centauri, got its name due to the fact that it is located closest to Earth. She is much more typical representative stellar community, despite the fact that this star is dim, red (and therefore cold) and small. It is located far from the main pair, about 300 times greater than the distance from the Sun to Pluto. If our Sun had a companion star like Alpha Centauri C, it would look like an ordinary star in the night sky. It could be observed with the naked eye, but it would not stand out against the background of other stars, moreover, it would seem dimmer.
Our cosmic neighbor is also Barnard's star, named after Edward Emerson Barnard, who lived about a century ago and is said to have been one of the keenest astronomers on earth. This modest little star is located towards the constellation Ophiuchus. It is the closest star that can be studied from the northern hemisphere using telescopes, but only a few astronomers are currently making such observations. Barnard's Star very reminiscent Proxima Centauri and according to the classification is a red dwarf, the most common type of star in the galaxy.
The mass of red dwarfs is about 10-30% of the mass of our Sun. Their own nuclear reactions proceed slowly, so their lifespan is 10 billion years. These stars are very interesting, and studying them helps to better understand our Sun. The outer layer of our Sun is a zone of convective energy transfer, and in red dwarfs these zones are more powerful and located deeper. In fact, some of these stars may be entirely convective. This leads to the generation of strong magnetic fields. When these fields rise above the red surface of stars, huge explosions can occur.
Stellar flares from dwarf stars are much more energetic than those that can be observed on our Sun. These stars were discovered because they flared brightly for several minutes. No wonder they got the name "flaring stars". Additionally, these giant stellar flares have been discovered to generate radio waves. They were first recorded by Manchester University professor Bernand Lovell in 1959, and later a new large telescope installed at the Jodrell Bank Observatory was used for this purpose. Many years ago, a young graduate student (namely myself) ( Let me remind you that this conversation is being conducted by David Whitehouse, approx. VC.) spent many sleepless nights studying the controls of this radio telescope in order to use new techniques to detect starbursts of red dwarfs in nearby space. Materials related to this work are kept in the library at Jodrell Bank.
One of the stars we studied did not want to reveal its secrets. During one year of observation there were many outbreaks, and the next year they were practically absent. I remember writing in my notebook, “Is the activity of this star similar to the 11-year cycle of the Sun?” May be.
Barnard's Star moves through space, and its apparent movement across the sky is the fastest of all. However, since this star is too small, its movement does not affect the shape of the constellations. The constellations seem immutable, and, from the point of view of man and the duration of his life, they are so. However, over the course of centuries, stars slowly change their position in space. For example, the period of revolution of our Sun and the planets of the solar system around the center of the galaxy is 200 million years. The process occurs so slowly that constellations that are 10 thousand years old are quite recognizable. However, if a modern astronomer were somehow transported back in time a million years, then, looking at starry sky, he would be confused. Barnard's Star moves across the sky at a speed of half a degree every 175 years. It is approaching and approximately in 11800 it will be close to Earth, at a distance of only four light years (closer than Proxima Centauri).
Many years ago, some astronomers believed that a planet was orbiting Barnard's Star. Observations showed that, as it moved across the sky, the star swayed slightly relative to its vertical axis. It is possible that this oscillation was caused by the action of gravity of one or more nearby major planets. However, no clear confirmation could be found, and the oscillation of the star itself was almost imperceptible. Over the past 10 years, the discovery has been made that there are many planets in the neighborhood of the solar system, revolving in orbits around their stars, i.e. is full of planets, and there is nothing unusual about it.
There is another red dwarf near the solar system, which became famous thanks to the television series “Star Trek”. This Star Wolf 359, which featured a spectacular battle between the United Federation of Planets and the Borg - a high-tech pseudo-race of cyborgs controlled by a single brain and increasing their numbers by assimilating entire worlds. Wolf 359 located in the constellation Leo and is the dimmest among its neighbors and one of the dimmest stars known to mankind. If the Sun were replaced by the star Wolf 359, there would either be no daylight, or it would be light that was only 10 times brighter than moonlight.
There are many more red dwarfs not far from Earth. Among them are Lalande 21 185 in the constellation Ursa Major. It is necessary to remember and UV China- a pair of red dwarfs and the prototype of the entire class of flare stars, which includes Proxima Centauri and Wolf 359. The distance between the stars of the pair UV China 6 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun, and the period of their revolution relative to each other is 25 years. Their total mass is only 30% of the mass of the Sun.
The most bright Star nearby Sun - Sirius, which is also called the Dog Star because it is located in the constellation Canis Major . In 1862 it was discovered that Sirius is a double star. Sirius A- a bluish-white star, it is 2 times larger than our Sun. Its surface temperature is 10,000 °C. Her little companion Sirius B the closest example of a white dwarf star to Earth. This is an extremely dense star that has completed its evolution and has shrunk to the size of a small planet. It is the same size as our Earth, but has the mass of the Sun. Its substance is so dense that a cup filled with it would weigh as much as a jetliner. Standing on its surface, you would weigh 100 times more than standing on Earth. These two are absolutely different stars rotate relative to each other with a period of 50 years, and the average distance between them is 20 times greater. The last of the stars known to us, the distance to which from Earth is less than 10 light years, was named Ross 154 and is, again, a red dwarf.
In 1783, William Herschel published his observations, which served as the impetus for the discovery of solar motion. He determined that our solar system is moving between neighboring stars in the direction of the star Lambda of Hercules, or Maasim, which means “wrist” in Arabic. To denote this direction, Herschel introduced the term apex (from the Latin “arech” - top), which began to mean a point on celestial sphere, in the direction in which the astronomical object is moving. The brightest star in the sky, Sirius, is the antiapex, i.e. the point in the direction from which the Sun moves.
This is the direction in which the Sun moves in its orbit around the center of the Milky Way. All 100 thousand stars of our Galaxy revolve around its center. The closer a star is to the center of the Galaxy, the faster it moves. As for our Sun, it is 24 thousand light years away from the center and moves in orbit at a speed of 220 km/s, making a full revolution in 230 million years. It turns out that during its existence the Sun circled the Galaxy about 18 times (according to other sources, 25-30 times). In addition to its circular motion around the center, the Sun also performs oscillatory movements up and down relative to the plane of the Galaxy. The oscillation period is 70 million years. This means that we pass through the median plane of the Galaxy every 35 million years. Some scientists compare this period with the interval between mass extinctions of living beings on Earth. It is no secret that the number of cosmic rays reaching the Earth has been increasing over the past 100 thousand years as the Earth approaches the median plane of the Galaxy. Perhaps this fact will affect cloudiness and, consequently, the Earth's climate.
Consisting of a series of spiral arms, our Sun is currently in a small spiral arm called Orion, which connects the larger spiral arms of Sagittarius and Perseus. The Earth passes through the main spiral arm every 100 million years, and the passage takes 10 million years. As it passes through the spiral arm, the influence of a nearby supernova increases, and its intense radiation, emitted even at a distance of tens of light years, can change the Earth's climate.
